Optical Design
The European Solar Telescope is based on a Gregorian on-axis configuration followed by a dioptric relay (Figure 1). The telescope is designed to achieve diffraction-limited performance and to deliver a telecentric F/50 science focal plane to the instruments, covering a field of fiew (FOV) of 90x90 arcsec2 and a wavelength range from 380 nm to 2300 nm.
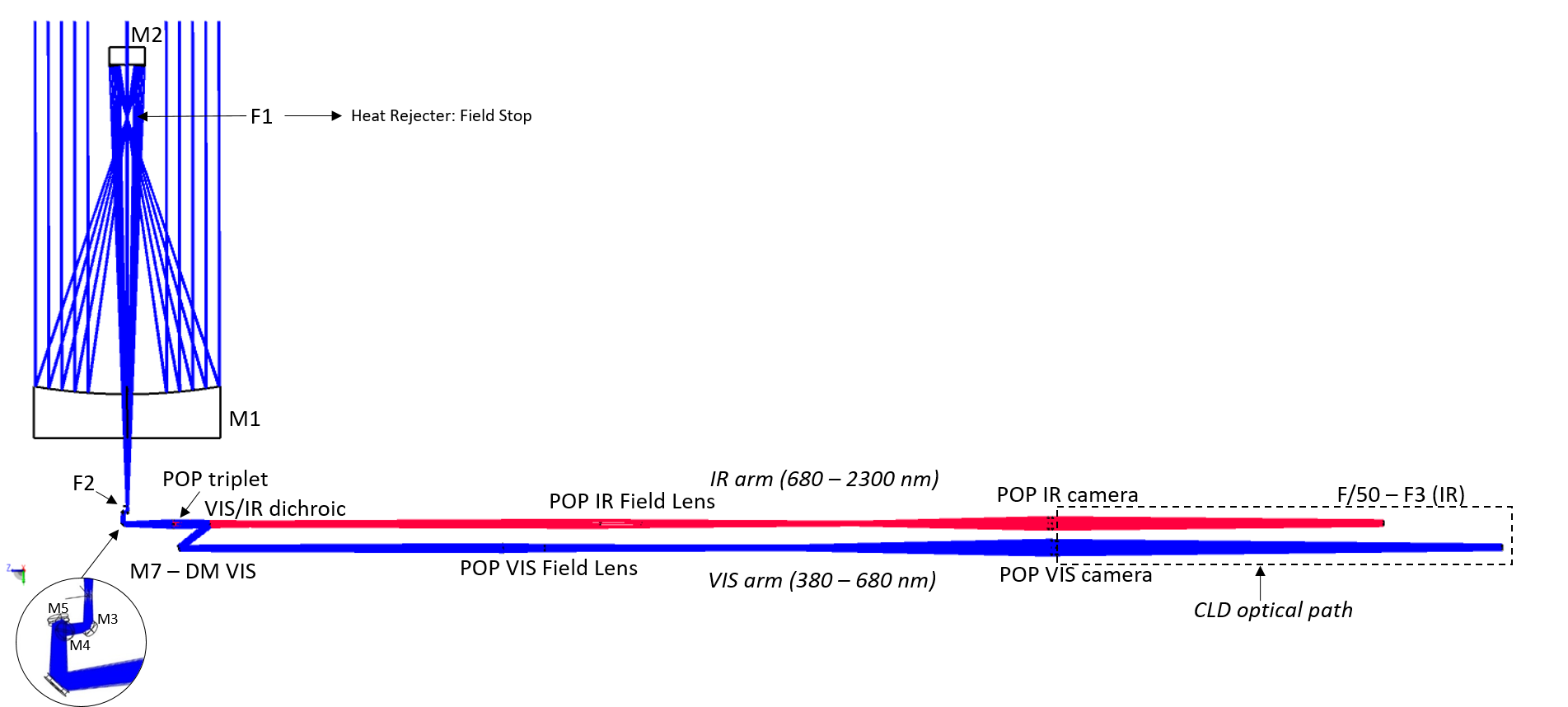
Figure 1. Optical layout of the telescope from the primary mirror to the F3 visible and near-IR foci. The telescope is pointing to the horizon in this diagram.
The telescope optics is divided into five subassemblies (see Figure 2):
- The telescope structure optics (M1 and M2), arranged in an on-axis Gregorian configuration.The stringent polarisation requirements of EST have led to the choice of a full on-axis design with M1 and M2 arranged in a Gregorian configuration. The on-axis design implies that M1 must have a central hole. On the other hand, the Gregorian configuration offers both a primary focus (F1) between M1 and M2, where light outside the science FOV can be rejected by a dedicated Heat Rejecter (HR), and an aplanatic secondary focus (F2). Recent improvements in the technology of Adaptive Secondary Mirrors (ASM) have made it possible to use an ASM for the secondary mirror (M2).
- The Transfer Optics and Calibration Assembly (TOCA), which is formed by the mirrors that generate the elevation and azimuth axes (M3 to M6), a Polarisation Calibration and Alignment (PCA) assembly, and the calibration assembly for the operation of M2.
- The Pier Optical Path (POP), defined by the refractive elements that transfer the light from the F2 focus to the science Coudé focus (F3). Inside the POP, visible (380 – 680 nm) and near-infrared (680 - 2300 nm) wavelengths are separated by a dichroic beamsplitter into different optical paths. M7 in the visible branch is a deformable mirror located at an intermediate pupil plane.
- The Coudé Light Distribution (CLD) system, composed of mirrors, dichroic and intensity beam splitters, provides each instrument located in the Coudé rooms with a science focus. Two visible and a near-infrared Coudé rooms exist with their corresponding CLD system and instruments.
- The Coudé Sensing Assembly (CSA), located in each Coudé room and formed by sensing instrumentation for the Adaptive Optics (AO) system, the calibration of the telescope and daily observations. There is a dedicated CSA in each Coudé room, designated as Coudé Vis/Red Sensing Assembly.
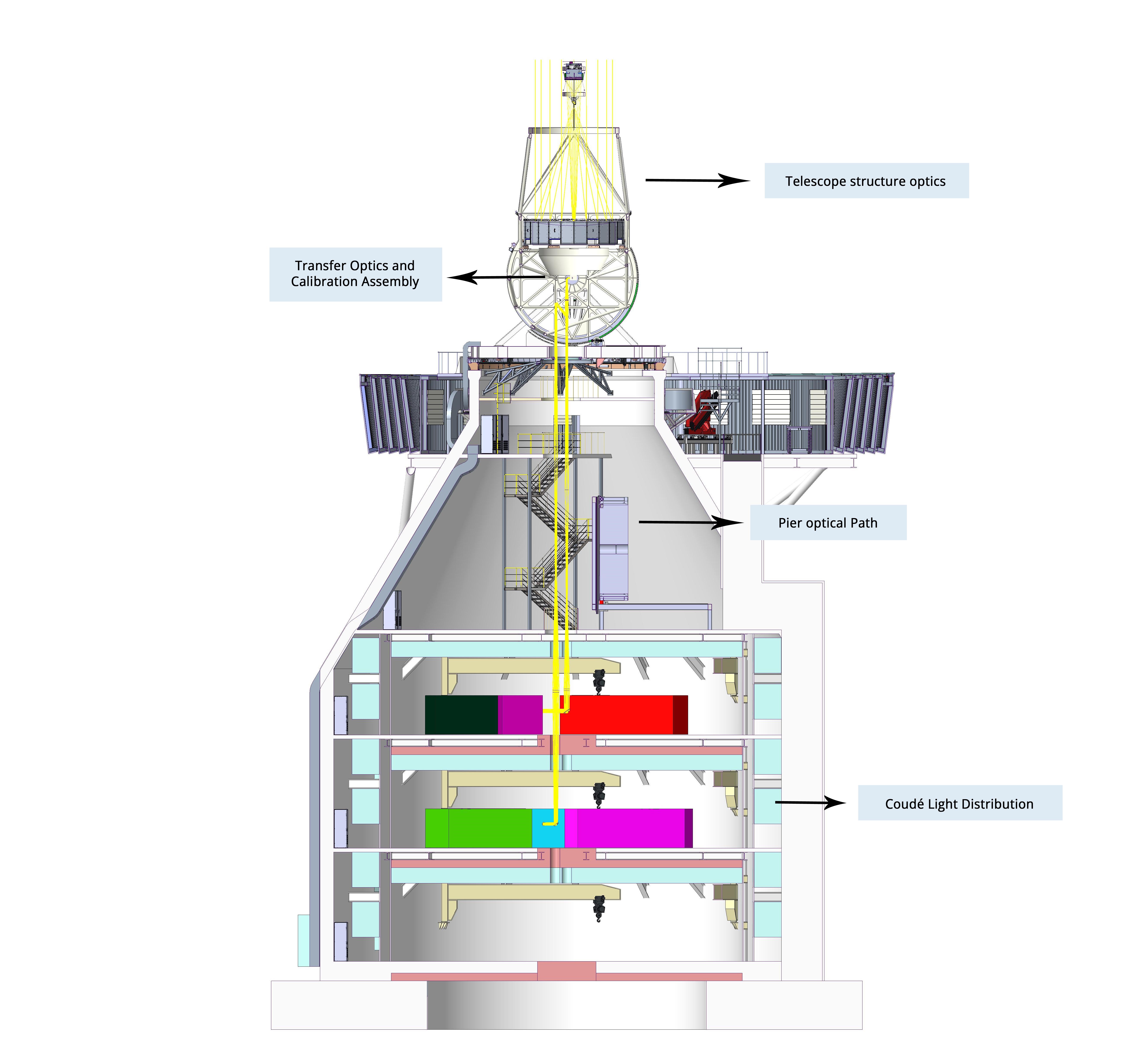 Figure 2. Telescope optics within the telescope structure and the building.
Figure 2. Telescope optics within the telescope structure and the building.
The EST optical configuration includes Adaptive Optics and Multi-Conjugated Adaptive Optics systems. Single Conjugated Adaptive Optics (SCAO) will be available at first light and will be gradually upgraded to MCAO, substituting M3 to M6 by deformable mirrors and adding an appropriate wavefront sensor.
The SCAO configuration includes M2 as an ASM for the IR arm and M7 as a deformable mirror for the VIS arm. The latter, which is part of the POP, will improve the AO correction to cope with the chromatic anisoplanatism induced by seeing (different atmospheric wavefront errors at different wavelengths). This effect is more noticeable at low elevation angles (below 25°). Having a dedicated deformable mirror for the VIS and another for the IR will also allow a differential correction of local seeing and vibrations for each arm to be made. This SCAO configuration requires the integration of two different wavefront sensors at CSA level (Red WFS and Vis WFS).
The EST design does not incorporate optical or mechanical de-rotation capabilities. Consequently, the change in orientation of the telescope over time during tracking, as well as the parallactic rotation of the Sun, implies that the image of the Sun recorded by the scientific instruments will rotate with a given instantaneous angular velocity. This rotation speed can be minimised through the proper orientation of the optical elements steering the telescope tracking system. Several design alternatives were evaluated to determine the best arrangement to minimise image rotation on the instrument detectors during the local morning.
