Coudé Light Distribution System
The Coudé Light Distribution (CLD) system is a set of optical components located downstream of the POP and distributed within the Coudé rooms. Its function is to adequately distribute the telecentric focal plane to each instrument that comprises the Scientific Instrumentation Suite (SIS).
One of the main goals of EST is to clarify the origin of the magnetic processes taking place in the solar atmosphere. To achieve this, EST must perform simultaneous spectro-polarimetric measurements in multiple spectral lines. To meet this goal, EST will be equipped with a range of instruments working simultaneously in different spectral intervals.
Two types of instruments are devised to fulfil the scientific objectives of EST:
- Tunable Image Spectropolarimeters based on Fabry-Pérot interferometers and Fixed-Band Imagers (TIS/FBIs).
- Grating spectrographs based on two integral field unit technologies: micro-lens arrays (IFS-M) and image slicers (IFS-S)
In addition to the science instruments, the Coudé rooms will also house wavefront sensing instrumentation that forms part of the CSA.
The Coudé rooms are distributed in two floors: the upper floor houses the infrared (IR) instrumentation, while the middle floor accommodates the visible (VIS) instrumentation.
The CLD distribution is represented in Figure 1. First, one fold mirror inside the VIS and IR Coudé rooms (VIS FM and IR FM), redirects the light coming from the corresponding POP arm towards each instrument. Two fixed dichroic beam splitters then divide the light from the VIS (380-680 nm) and IR (680-2300 nm) arms into two spectral sub-arms each: blue (380-500 nm), visible (500-680 nm), red (680-1000 nm), and infrared (1000-2300 nm).
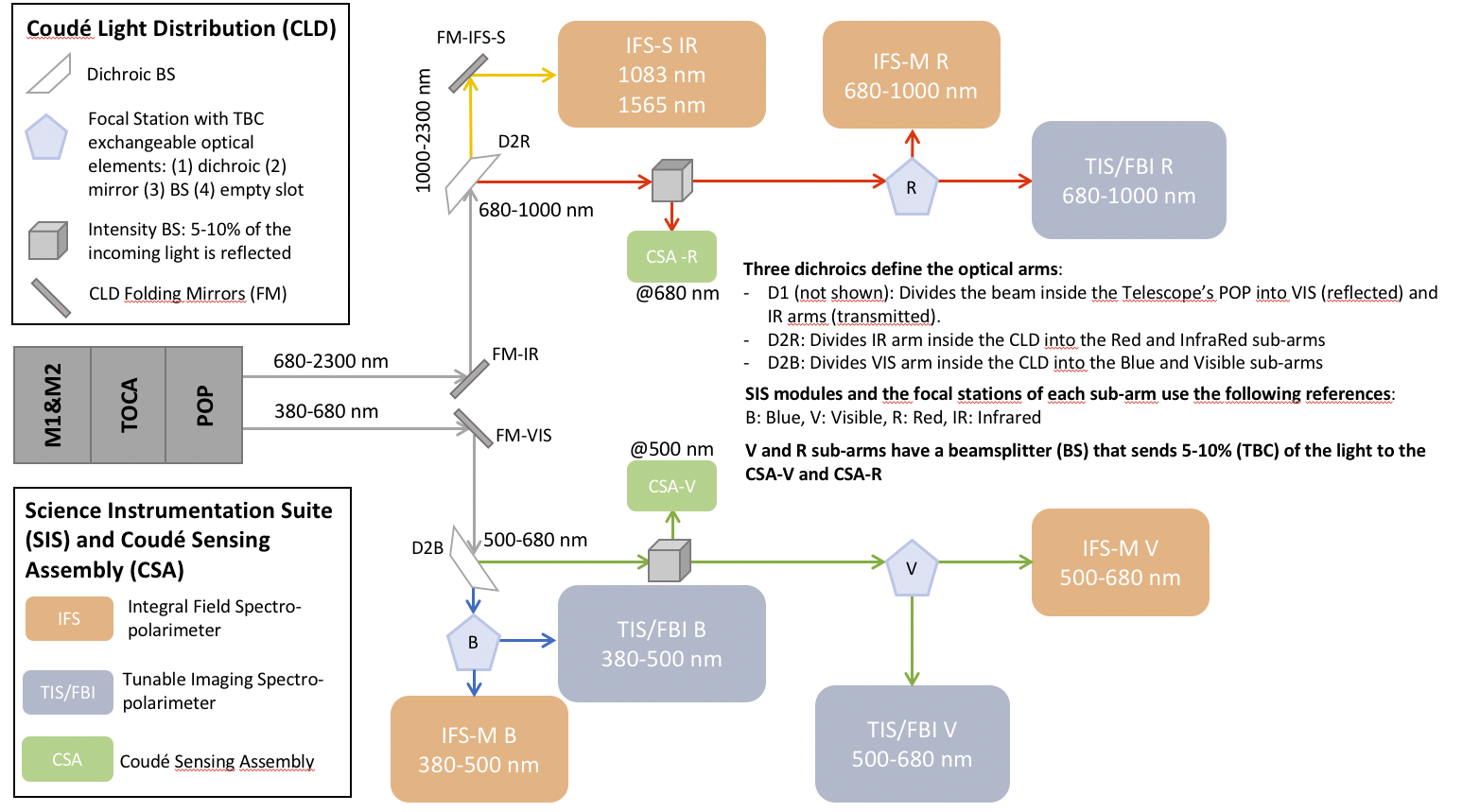 Figure 1. CLD system for first-generation instruments.
Figure 1. CLD system for first-generation instruments.
Along each sub-arm, except in the IR sub-arm, there are interchangeable optical components including mirrors, beam splitters, dichroic elements, and empty slots or plates which can be switched to deliver the beam to the different instruments. In the VIS and IR sub-arms, intensity beam splitters pick off 5-10% of the incoming light to feed the CSA, which includes wavefront sensors, a tip-tilt camera (Red sub-arm) and a full field camera (VIS sub-arm).
The use of interchangeable elements allows for two observation modes in three sub-arms for those instruments that share a given spectral range (namely the blue, visible and red sub-arms):
- Single-Mode Operation: Delivers all the incoming light across the entire wavelength range of the sub-arm to one type of instrument.
- Dual-Mode Operation: Splits the light between two types of instruments in the same sub-arm, using either a dichroic or intensity beam splitter at the focal station.
The infrared sub-arm always operates with a single instrument, which receives the full intensity and spectral range of light.
This flexible design allows for an efficient and versatile operation, supporting a range of scientific observations and instrumental needs.
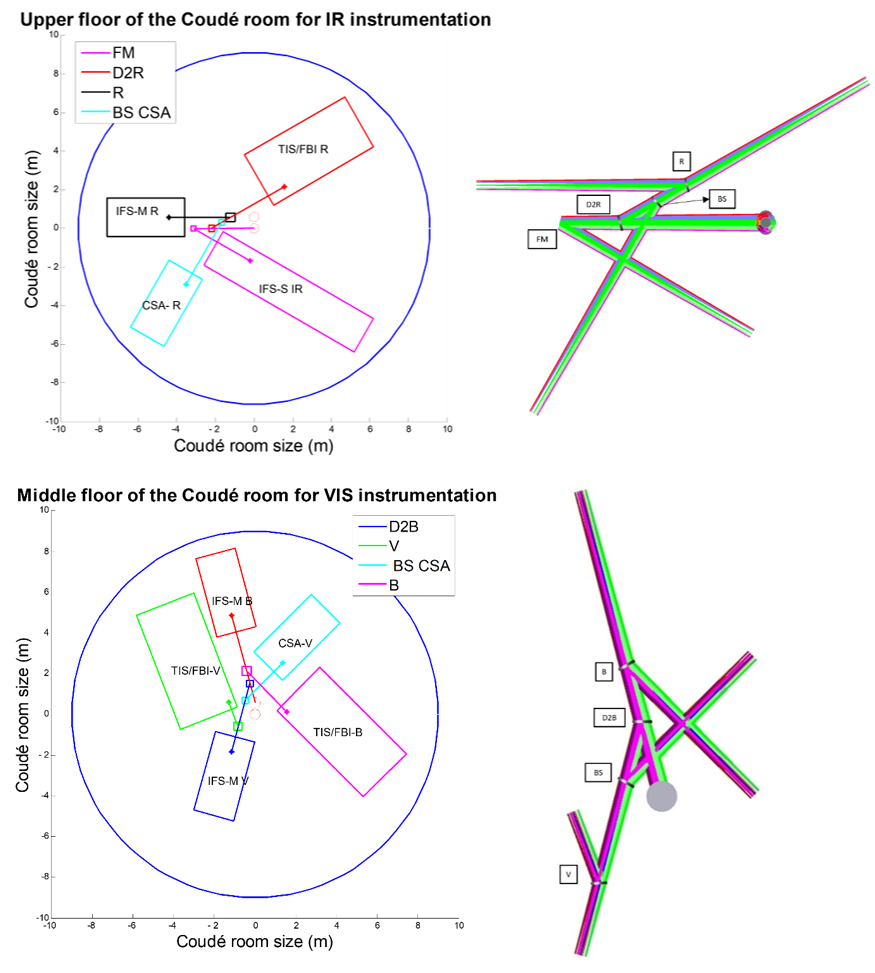 Figure 2. Physical distribution of the first-generation IR and VIS instruments in the Coudé rooms (top and bottom panels, respectively).
Figure 2. Physical distribution of the first-generation IR and VIS instruments in the Coudé rooms (top and bottom panels, respectively).
